see edema.
Edema (American English), also spelled oedema (British English), and also known as fluid retention, dropsy and hydropsy, is the build-up of fluid in the body's tissue, a type of swelling. Most commonly, the legs or arms are affected. Symptoms may include skin that feels tight, the area feeling heavy, and joint stiffness. Other symptoms depend on the underlying cause.
| Edema | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Oedema, œdema, fluid retention, water retention, dropsy, hydropsy |
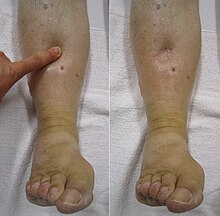 | |
| "Pitting" edema | |
| Pronunciation | |
| Specialty | Cardiology, nephrology |
| Symptoms | Skin which feels tight, area may feel heavy |
| Usual onset | Sudden or gradual |
| Types | Generalized, localized |
| Causes | Venous insufficiency, heart failure, kidney problems, low protein levels, liver problems, deep vein thrombosis, lymphedema |
| Diagnostic method | Based on a physical exam |
| Treatment | Based on cause |
Causes may include venous insufficiency, heart failure, kidney problems, low protein levels, liver problems, deep vein thrombosis, infections, angioedema, certain medications, and lymphedema. It may also occur in immobile patients (stroke, spinal cord injury, aging), or with temporary immobility such as prolonged sitting or standing, and during menstruation or pregnancy. The condition is more concerning if it starts suddenly, or pain or shortness of breath is present.
Treatment depends on the underlying cause. If the underlying mechanism involves sodium retention, decreased salt intake and a diuretic may be used. Elevating the legs and support stockings may be useful for edema of the legs. Older people are more commonly affected. The word is from the Ancient Greek οἴδημα oídēma meaning 'swelling'.
